
©2024 FAN SEPARATOR GmbH
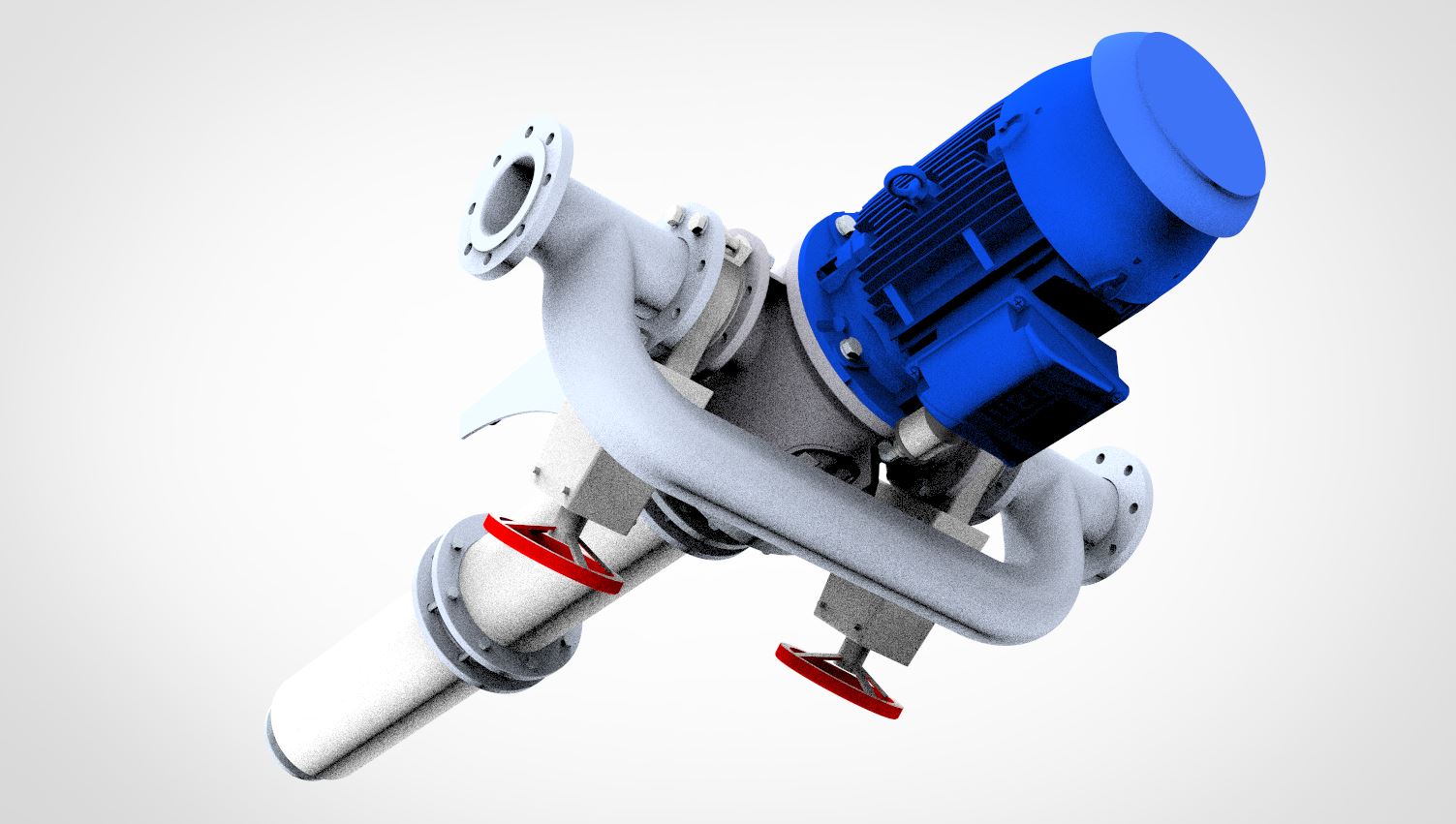
As a relatively inexpensive process, the mechanical separation of solids from liquids is an increasingly important aspect of the recirculation of production water and the treatment of waste water.
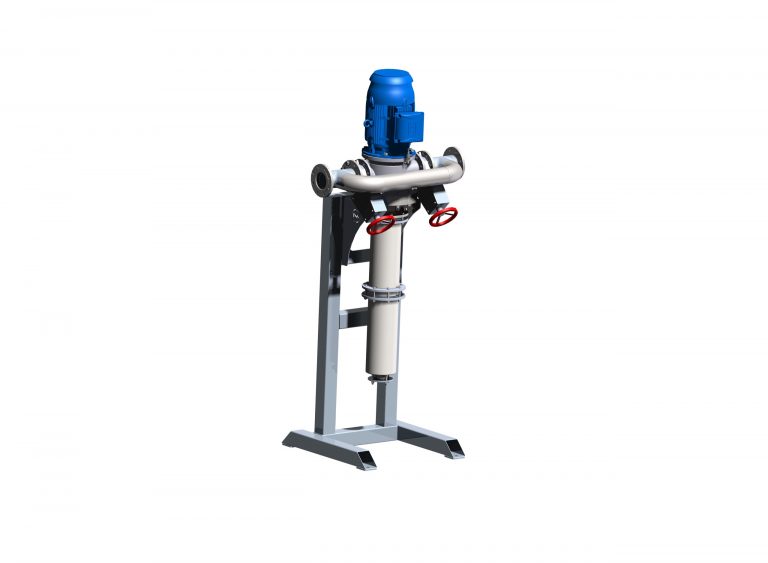

The FAN CCS separator was developed for the treatment of turbid fluids containing particles with high or low specific weight. The particle size must be lower than about 2 mm. The separator is therefore particularly well suited for the treatment of turbid media that have already been sieved or otherwise filtered to remove the coarse particles.
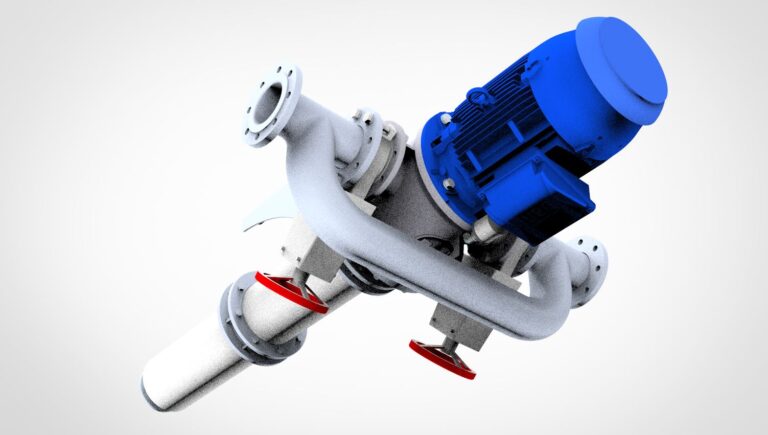
One shared feature of sludge separation via centrifugal separators and hydrocyclones is that the pretreated turbid medium is introduced at high velocity into a separation chamber, where an intensely rotating field of flow is produced. According to the specific weights of the fluid and the sediment, the fractions are separated within the centrifugal field into the effluent and the sedimentation sludge.
The heavy particles are first carried down by the flow within the cylindrical portion of the system, then forces arising from the decreasing radii of the tapered wall take them down to the sludge output. The low specific weight particles are moved to the centre of the cone by the centrifugal field.
The effluent leaves the centrifugal separator via the centre. The special feature of the FAN CCS is that the drive systems for transporting the liquid with the transport rotor and for generating the centrifugal field with the cyclone rotor are situated on a common axis and integrated into the centrifuge. A stator is located in-between. This eliminates the need for a separate pump for feeding in the suspension as well as for pipes and fittings outside of the centrifugal separator. Plus, it is possible to introduce a more powerful rotational force with the cyclone rotor, which is necessary for good separation performance.

Call us:
+499227938400
E-Mail us:
info@fan-separator.de
https://www.facebook.com/fanseparator